Technologies
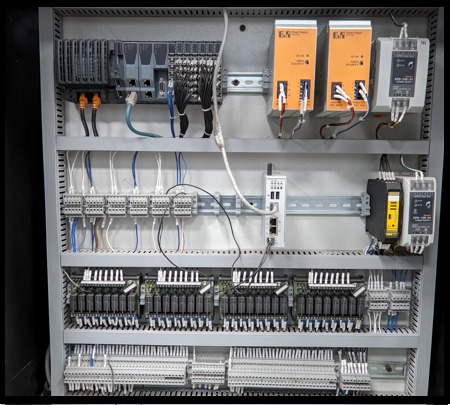

Industrial IoT and Cyber Physical Systems
The integration of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and Industrial IoT is transforming traditional manufacturing. By merging the physical and digital worlds, CPS enables seamless communication between smart devices, leading to autonomous production processes, real-time data sharing, and optimized resource management. This shift allows manufacturers to build adaptive, connected, and efficient production systems, revolutionizing the way industries operate.
CPS forms the backbone of modern smart manufacturing, driving innovation and enabling new business models through intelligent automation and data-driven decision-making.
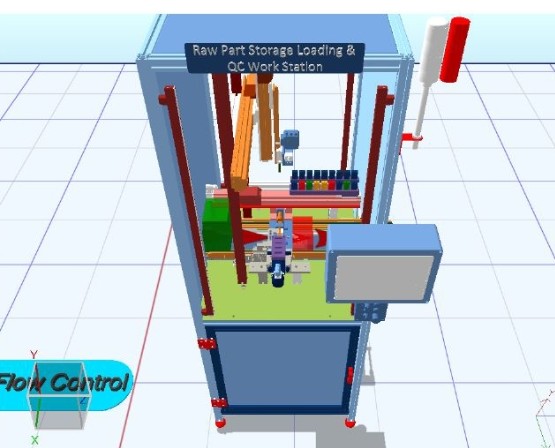
Advance Simulation and Digital Twin
Advanced Simulation allows manufacturers to create digital models of production systems, optimizing performance and running "what-if" scenarios without impacting real-world operations. These tools help enhance decision-making, streamline production, and improve resource utilization.
The Digital Twin concept takes it further by creating a virtual counterpart of a physical system, using real-time data to monitor, optimize, and predict performance. This innovation accelerates time-to-market, improves product quality, and reduces operational costs.

Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots (cobots) are transforming manufacturing by working safely alongside human operators without the need for physical barriers. They enhance efficiency, precision, and safety, while being easily programmable and adaptable to different tasks. Cobots are lightweight, mobile, and ideal for applications like assembly, machine tending, quality inspection, and more.
With integrated safety features and quick re-tasking abilities, cobots are a key element of the smart factory and are driving the evolution of Industry 4.0.

Rapid Prototyping and Tooling
3D printing revolutionizes manufacturing by enabling companies to go directly from digital design to final production without the need for traditional tooling. This technology supports cost-effective low-volume production, customization, and on-demand printing, which reduces inventory and shortens lead times. From prototypes to components and tools, 3D printing is reshaping industries like automotive, healthcare, and aerospace.

Extended Reality (XR)
Extended Reality (XR), including Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR), is transforming manufacturing by offering immersive solutions for training, maintenance, and operations. XR technologies provide real-time data, virtual simulations, and interactive 3D environments, enhancing productivity, safety, and collaboration across smart factories.
By integrating XR with Industry 4.0 technologies, manufacturers can optimize workflows, reduce errors, and create more efficient and flexible operations.

Smart Sensors, Actuators and Controllers
Smart sensors and actuators are the backbone of the smart factory, providing real-time data and enabling communication between machines and control systems. These technologies enhance efficiency, enable predictive maintenance, and automate tasks through intelligent sensing, diagnostics, and seamless system integration.
With features like web-based commissioning and multi-protocol communication, smart sensors and actuators drive the next level of industrial automation in Industry 4.0.
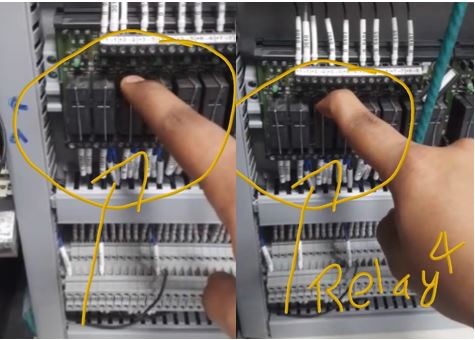
Remote Maintenance
Remote maintenance allows service technicians to support customers from anywhere, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency. By remotely accessing machines, technicians can diagnose issues in real-time and prepare necessary tools or parts, ensuring faster repairs. This also enables predictive maintenance, where real-time data is analyzed to prevent failures before they occur, optimizing machine performance.
Remote maintenance is key to efficient operations in Industry 4.0, providing faster response times, cost savings, and improved customer service.

Industrial Safety
Industrial safety ensures the protection of workers and the environment by managing risks in machinery and plant operations. Traditional safety systems rely on hardware-based solutions like relays and shutdowns, which can disrupt production. Modern dynamic safety concepts offer a more flexible approach, allowing processes to continue safely without immediate shutdowns and reducing downtime.
Integrating functional safety into smart manufacturing systems from the planning stage is essential for achieving both safety and productivity in Industry 4.0 environments.
